|
تضامنًا مع حق الشعب الفلسطيني |
فرقد (نجم)
| فرقد | |
|---|---|
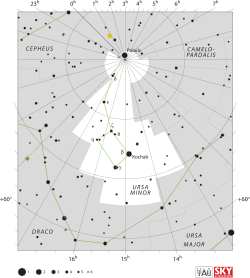
نجم فرقد في كوكبة الدب الأصغر (γ)
| |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة J2000.0 اعتدالان J2000.0 |
|
| كوكبة | الدب الأصغر |
| مطلع مستقيم | 15س 20د 43.71604ث[1] |
| الميل | ° +71 ′50 ″02.4596[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | +3.05[2] |
| الخصائص | |
| نوع الطيف | A2 III[3] |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | +0.08[2] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | +0.09[2] |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة الشعاعية (Rv) | −3.9[4] كم/ث |
| الحركة الخاصة (μ) | −17.73[1]+17.90[1] |
| التزيح (π) | 6.70 ± 0.11 د.ق |
| البعد | 487 ± 8 س.ض (149 ± 2 ف.ف) |
| القدر المطلق (MV) | –2.84[5] |
| تفاصيل | |
| نصف قطر | 15[6] نق☉ |
| ضياء | 1,100[6] ض☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | 2.53[7] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 8,280[8] ك |
| سرعة الدوران (v sin i) | 180[9] كم/ثا |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| Pherkad, Pherkad Major, Gamma Ursae Minoris, 13 Ursae Minoris, فهرس النجم الساطع 5735, مسح بون الفلكي+72°679, فهرس هنري درابر 137422, فهرس مرصد سميثسونيان للفيزياء الفلكية 8220, هيباركوس 75097 | |
| قاعدة بيانات المراجع | |
| سيمباد | بيانات |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
فرقد أو Gamma Ursae Minoris اسمه التقليدي Pherkad مشتق من الاسم العربي.[10]}} وهو نجم متغير في مجموعة الدب الأصغر المتحركة ويشكل مع نجم الكوكب نهاية حوض كوكبة الدب الأصغر.
يملك قدر ظاهري +3.00 ويبعد حوالي 480 سنة ضوئية عن الأرض وينتمي إلى الفئة الطيفية A3 مما يعني أن درجة حرارة سطحه تتراوح ما بين 7,500 إلى 11,000 كلفن.[11]
انظر أيضا
المراجع
- ^ أ ب ت ث van Leeuwen، F. (نوفمبر 2007)، "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 474، ص. 653–664، arXiv:0708.1752، Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
- ^ أ ب ت Fernie، J. D. (مايو 1983)، "New UBVRI photometry for 900 supergiants"، Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series، ج. 52، ص. 7–22، Bibcode:1983ApJS...52....7F، DOI:10.1086/190856
- ^ Abt، Helmut A.؛ Morrell، Nidia I. (1995). "The Relation between Rotational Velocities and Spectral Peculiarities among A-Type Stars". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. ج. 99: 135. Bibcode:1995ApJS...99..135A. DOI:10.1086/192182.
- ^ Wielen، R.؛ وآخرون (1999)، "Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions"، Veröff. Astron. Rechen-Inst. Heidelb، Veröffentlichungen des Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg، ج. 35، Bibcode:1999VeARI..35....1W
- ^ Verdugo، E.؛ وآخرون (نوفمبر 2005). "Do A-type Supergiants have Magnetic Fields?". في Ignace، Richard؛ Gayley، Kenneth G. (المحررون). The Nature and Evolution of Disks Around Hot Stars; Proceedings of a meeting held 7-9 July 2004 in Johnson City, Tennessee, USA. The Nature and Evolution of Disks Around Hot Stars. ASP Conference Series. ج. 337. ص. 324. Bibcode:2005ASPC..337..324V.
- ^ أ ب Kaler، James B.، "Pherkad (Gamma Ursae Minoris)"، Stars، University of Illinois، مؤرشف من الأصل في 2019-04-28، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2007-10-05
- ^ Hauck، B.؛ Jaschek، C. (فبراير 2000)، "A-shell stars in the Geneva system"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 354، ص. 157–162، Bibcode:2000A&A...354..157H
- ^ Zorec، J.؛ وآخرون (يوليو 2009)، "Fundamental parameters of B supergiants from the BCD system. I. Calibration of the (λ_1, D) parameters into Teff"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 501، ص. 297–320، arXiv:0903.5134، Bibcode:2009A&A...501..297Z، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361/200811147
- ^ Royer، F.؛ وآخرون (أكتوبر 2002)، "Rotational velocities of A-type stars in the northern hemisphere. II. Measurement of v sin i"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 393، ص. 897–911، arXiv:astro-ph/0205255، Bibcode:2002A&A...393..897R، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:20020943
- ^ "Simbad Query Result". Simbad. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2016-03-15. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2007-10-05.
- ^ "Pherkad". Simbad. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2008-12-02. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2007-10-05.